Procedure and Information on Abortion by D&C
🏥 Abortion Methods: What Do I Need to Know? — Quiz
- A D&C is a surgical procedure in which the uterus is scraped out with a blunt scraper (curette).
- It is used as a surgical abortion method but is also performed for other medical reasons.
- A D&C entails several risk factors — such as infection.
Below you will find pertinent information on D&C abortions, how they work, and what your next steps might be.
What Is Dilation and Curettage?
As part of the woman's natural menstrual cycle, her uterine lining thickens every month. If a pregnancy does not occur within the cycle, this lining is subsequently shed
during menstruation.
In a D&C (dilation and curettage), the uterus is scraped, and the uterine lining is cleared surgically using a blunt, spoon-shaped scraper (curette).
Abortion Methods: What do I need to know? — Quiz
Is this question weighing on you? Answer three multiple-choice questions about your personal situation and receive a professional evaluation within seconds on your screen.
D&C as an Abortion Method
In addition to its other uses, dilation and curettage can be used in abortions between the 5th and the 16th week of pregnancy.
Today, D&C abortions are becoming more uncommon. Most doctors prefer vacuum aspirations (suction aspirations) since this procedure is less time-consuming and less likely to lead to complications.
According to SCDHEC, 7.9% of abortions were performed by dilation and curettage in 2021.
ℹ️ Sometimes, a D&C is necessary after a medicinal abortion or vacuum aspiration abortion if tissue is left in the uterus following these procedures. A D&C is then performed to prevent an infection.
⬇️ Skip to details about the procedure.
Diagnostic Reasons
Dilation and curettage is most commonly used in the diagnostic evaluation of abnormal bleeding
(e.g., very heavy, very long, painful, or irregular menstrual bleeding). In this case, the uterine lining is removed. Possible reasons for abnormal bleeding may be fibroids or polyps, both of which are benign growths in the uterus.
Abnormal findings during a routine ultrasound of the uterus or a pap smear provide another
reason for a D&C. Dilation and curettage is performed in order to determine whether a uterine growth is malignant.
Therapeutic Reasons
Dilation and curettage is also occasionally used as a therapeutic method, for example, if menstrual bleeding is too heavy or prolonged or when bleeding during or after menopause.
After a Miscarriage or Birth
Dilation and curettage may also be necessary after a miscarriage. In this case, possible remnants of the embryo and placenta are removed from the uterus by a D&C. Leaving them could lead to an infection or uterine adhesions.
Sometimes a D&C may also be necessary after a healthy and natural birth. If parts of the placenta do not detach entirely and remain in the uterus, the mother may become septic. Dilation and curettage should then be performed promptly. Otherwise, the uterus cannot properly regress and shrink to its original size.
D&C Abortion: Step-by-Step
A D&C abortion is usually an outpatient procedure that is performed under sedation or
local anesthesia. The procedure takes about ten minutes.
Procedure
- The doctor first inserts a so-called speculum into the vagina. A speculum has two blades that form a funnel-shaped opening. The vagina can be spread open, and the cervix becomes visible, spreading the two blades.
- The cervix is stretched using special pins called Hegar dilators to access
the uterine cavity. - Then, using a blunt curette (spoon-like instrument), the embryo and the placenta are detached from the uterine wall and removed from the uterus.
After the Surgery
After the surgery, the doctor performs an ultrasound to ensure that the removal of embryo and
placenta is complete.
Post-D&C Abortion Information and Instructions
After the procedure, light vaginal bleeding may occur for several days. This bleeding may become heavier after about three to five days, comparable to menstrual bleeding. Some women may
experience soreness similar to menstrual cramps. A bloody discharge may continue for about 14 days until the next menstrual period.
Most healthy women start their menstrual period about 4-8 weeks after the procedure. However, it is possible to become pregnant even before menstruation. It is advisable to wait three months before considering another pregnancy.
Additionally, the following activities should be avoided for about three weeks after the procedure, as the cervix is still slightly open due to the dilation. Germs could otherwise enter the uterus, causing infection:
- Sexual intercourse
- Tampons
- Bathing/swimming
- Sauna visits
D&C Risk Factors
In rare cases, a curettage may entail complications. Your doctor will discuss these with you before the procedure.
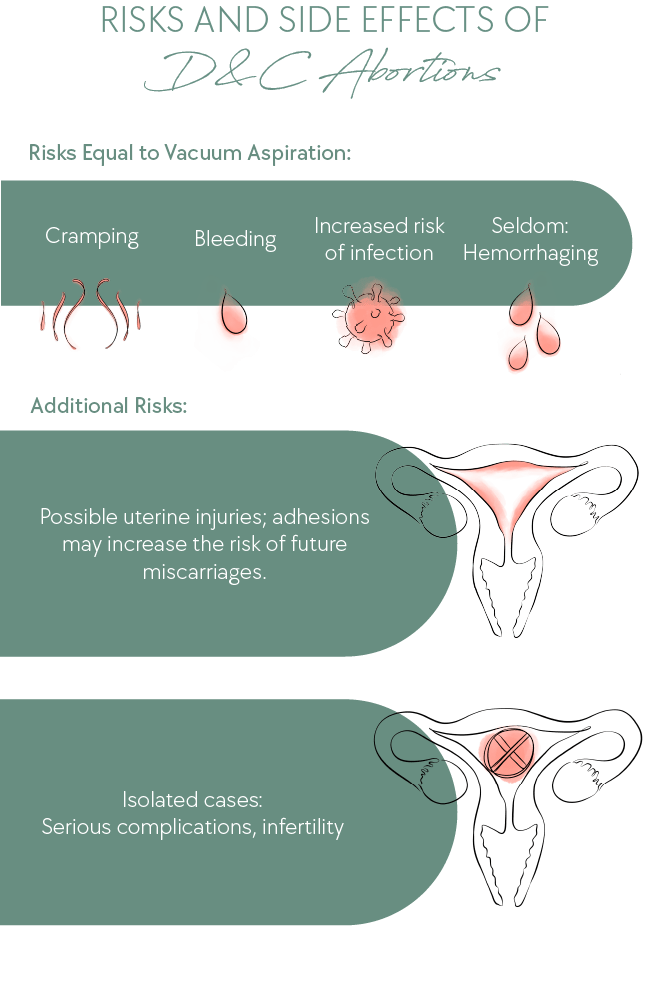

ℹ️ For more information, go to Risks and Side Effects of Abortion.
Apart from considering the rare potential physical risks of an abortion, stay in tune with your heart and mind to evaluate whether this is the right path for you.
- Read more about the Potential Emotional Effects of an Abortion.
Should I Get an Abortion? If You Are Facing This Question...
Perhaps your pregnancy has placed you in a difficult situation, which causes you to consider an abortion. You are now looking into possible methods. There are probably an overwhelming amount of questions running through your mind.
Apart from your thoughts about abortion methods, you are probably dealing with a whole other set of worries and concerns. It would be hard to know where to start.
Take a deep breath! You do not have to decide on the spot. You are usually given plenty of time to make a choice. Find out about legal time limits in your area at Until When Can I Have an Abortion?
Allow us to walk alongside you, providing you with a judgment-free environment where you can find the path that is right for you.
- ⛑ Where do I go from here? — Quick Answers Quiz
- ⚖️ Wondering whether to have an abortion or not? Take the Abortion Test